| 基 本 信 息 | ||
| CAS编码 | 79-11-8 | |
| Development Codes | ||
| IUPAC名称 | ||
| 英文通用名称 | Chloracetic acid | |
| 中文通用名称 | 氯醋酸 [进入食品百科查看-- 氯醋酸 的信息] | |
| 英文商品名称 | Monochloroacetic acid | |
| 中文商品名称 | ||
| 英文化学名称 | Acetic acid, chloro- | |
| 中文化学名称 | 一氯代乙酸 | |
| 理 化 性 质 | ||
| 分子式 | C2-H3-Cl-O2 | |
| 结构式 |
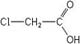
|
|
| 分子量 | 94.5 | |
| 性状描述 | 无色斜方结晶,具吸湿性,有三型:α体mp63℃;β体mp55-56 ℃;γ体mp50℃。液体bp189℃。易溶于水,可溶于苯、氯仿、乙醇和乙醚。工业品纯度约90%,mp61-63℃。钠盐为白色无味结晶固体,20℃下溶于水85g/100ml。 | |
| 毒 理 学 性 质 | ||
| LD50/LC50 | 急性口服LD50,大白鼠76mg/kg,小白鼠165mg/kg。人口服致死最低量,50mg/kg。小白鼠皮下注射中毒最低量,100mg/kg。大白鼠皮下注射LD50,5mg/kg。小白鼠腹腔注射致死最低量,500mg/kg。钠盐急性口服LD50,大白鼠650mg/kg,小白鼠165mg/kg。 | |
| NOEL |
Study Chemical Name : Chloroacetic acid Purity Grade : >99% Vehicle - Solvent : Water Test Substance Test method : description GLP: no Test Method and Conditions IRPTC Data Profile 196 Mammalian Toxicity Exposure Type : SHORT Exposure Period : Dose / Concentration : Exposure 14 d 265-482 mg/kg BW/d Exposure comments : Groups of mice received 0, 265, 386 or 482 mg/kg of chloroacetic acid in drinking water. BW NEF Affected in Organ Effect Rev. OnSet Sex Exposed - Controls --------- ----------- ------- ------------------- ------- ----------------------------- Mice body and relative liver weights were not altered. NEF Proliferation of peroxisomes did not occur. NOEL NOEL: 482 mg/kg |
|
| NOAEL | ||
| LOAEL | ||
| ADI | ||
| BMD | ||
| PTWI | ||
| PTDI | ||
| RfD | ||
| MTD | ||
| Acute RfD | ||
| 是否致癌物 | × | |
| 是否基因致癌物 | × | |
| 其他毒理学性质 | Toxicity 7.2.1 Human data 7.2.1.1 Adults Skin exposure It can be difficult to determine at an early stage the percentage of body burns, due to irregular or rather blotchy vasoconstriction that seems to be typical of MCA burns. 2 or 3 days later skin burns may be up to 50% larger than at first glance (Vincenti, 1987). up to 5% body surface possibly moderate (80% solution) systemic poisoning 6-10% body surface (molten 80°C) severe, up to lethal systemic poisoning approx 10% body surface moderate (90% solution) systemic (Kusch et al 1990) poisoning 15% body surface (80% solution) lethal (Millischer and Ruty, 1986; systemic Contassot et al., 1987; poisoning Vincenti, 1987) 25-30% body surface (80% solution) lethal (Kulling et al., 1992) systemic poisoning unknown % body surface lethal + inhalation systemic (von Oettingen, 1958; poisoning Zeldenrust, 1951) 7.2.1.2 Children No data available 7.2.2 Relevant animal data Prolonged inhalation of MCA vapours in rats induced breathing difficulties, decreased oxygen consumption, haemoconcentration and inflammatory reaction of the bronchial tree (Maksimov & Dubinina, 1974). LD50 MCA (oral) (rat, mouse) 55 to165 mg/kg (Hayes et al., 1973; Huismanss et al., 1986; Maksimov & Dubinina, 1974; RTECS 1986; Woodard et al., 1941). LD50 MCA (oral) (mouse) 260 mg/kg (Berardi et al., 1987). LD50 Na-MCA (oral) (rat, mouse, guinea pig) 76.2 to 255 mg/kg (Huismanss et al., 1986; Maksimov & Dubinina, 1974; Woodard et al., 1941). LD50 MCA (skin, rabbit) 230 mg/kg (Vernot et al., 1977). In one study degeneration of Purkinje cell nuclei was noted probably indicating blood-brain barrier damage (Berardi et al., 1987). 7.2.3 Relevant in vitro data In vitro studies have shown that MCA toxicity still occurs in spite of incubation of the cells with acetate or acetate donors (van Hinsbergh, 1994). 7.2.4 Workplace standards 1 mg/m3 (OEL-Russia STEL 1993); 8-hr TWA: 0.3 ppm, skin (AIHA 1996) Ceiling or short-term TWA: 1 ppm, 15 min (ACGHI 1986) 7.2.5 Acceptable daily intake (ADI) Unknown. | |
| 应 用 情 况 | ||
| 国内应用情况 | 国内登记或注册 | × |
| 国内生产 | × | |
| 国外进口 | × | |
| 国外应用情况 | 无 | |
| 其 他 信 息 | ||
| 类别 | 芽前除草剂 | |
| 作用 | 芽前除草剂。有接触作用。能产生药害。防治甘蓝、洋葱、青葱等田间杂草。甘蓝类用药量为20-25kg ai/ha。 | |
| 作用特点 | 无 | |
| 代谢情况 | Metabolism It has been suggested that MCA binds to gluthathione-S-transferase (GST) rather than to glutathione (Dierckz, 1984), while others suggest that MCA binds to glutathione or other sulfhydryl containing substances (Dalgaard-Mikkelsen et al., 1955; Fuhrman et al., 1955;Gosselin et al., 1984; Hayes et al., 1973; Hirade et al.,1950; Huismanss et al., 1986; Yllner, 1971). Another author suggests that the main metabolites (in mice) were non-conjugated S-carboxymethyl cysteine, thio-diacetic acid, and some glycolic acid and suggests the following metabolic pathway for chloroacetate in mice: CH2Cl-COOH --> (CH2OHCOOH --> (CO2 MCA glycolic acid ' ' COOH-COOH "CH2NH2COOH" oxalic acid "G-S-CH2COOH S-carboxymethyl glutathione" ' HOOC-CH(NH2)CH2SCH2COOH S-carboxymethyl cysteine ' HOOC-CH2-S-CH2-COOH thio-diacetic acid Compounds in " " were not isolated (Huismanss et al., 1986, Yllner, 1971) Glycolic acid is metabolised in man to glyoxylic acid, which is metabolised to formic acid, glycine and oxalic acid (Jacobsen et al 1984). Elimination and excretion In one human case the majority of MCA was excreted as nonmetabolized MCA. A minor part reacted with glutathione and was excreted in urine as the conjugate. A small amount was metabolized and excreted as carbon dioxide in exhaled air (Dancer et al., 1965). In mice 80-90% of administered MCA was excreted in urine within 24 hours, probably as metabolites, 8% was excreted via exhaled air as CO2 (Yllner, 1971). | |
| 日本肯定列表 | ||
| 相关标准 | ||
| 相关资料 | ||
| 相关讨论 | ||
| 相关限量 | ||
| 相关农药 |
|
|
| 备注 | 无 | |
 |
| 